Cpu Stress Test 80 Degrees – What You Should Know!
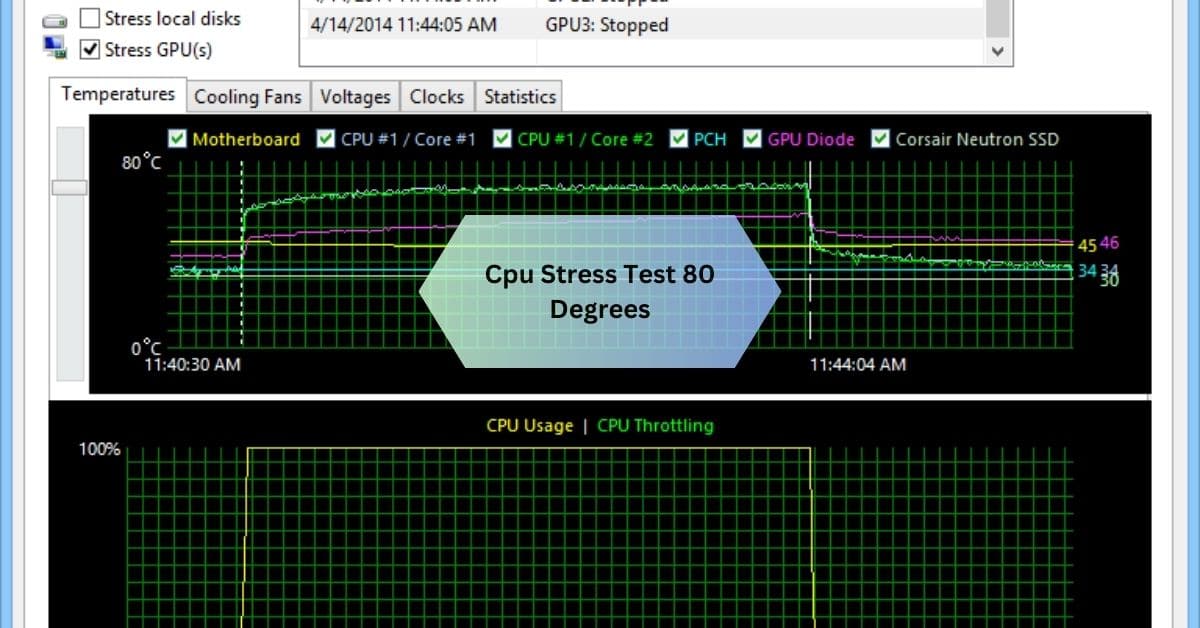
I recently ran a CPU stress test, and my system hit 80 degrees Celsius after just a few minutes. It made me a bit nervous, but I was relieved to see that my cooling setup kept the temperature stable without throttling.
A cpu stress test 80 degrees Celsius is generally safe for most modern processors but indicates your cooling system is working hard. Ensure proper airflow and thermal paste to maintain stable performance during extended tests.
Stay tuned with us as we dive into everything about CPU stress tests hitting 80 degrees—what it means for your system, how to manage temperatures, and tips to optimize performance!
Understanding CPU Stress Tests!
Modern CPUs are highly capable and reliable, but to ensure they perform optimally under demanding workloads, stress testing is essential. A CPU stress test pushes your processor to its limits, uncovering its maximum performance potential, thermal characteristics, and stability.
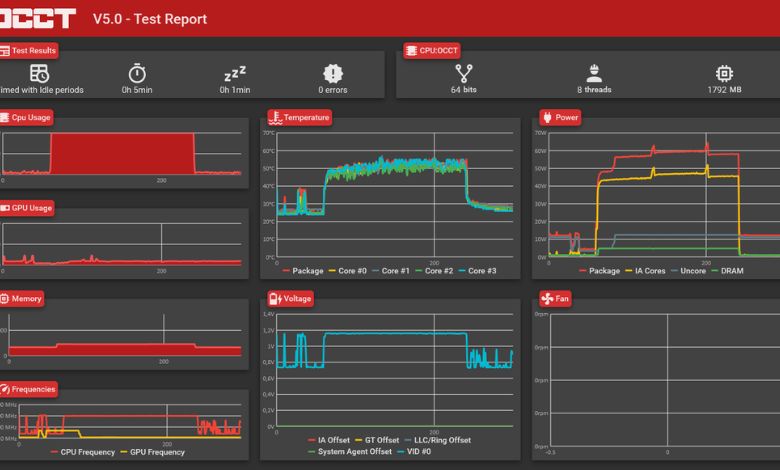
What is a CPU Stress Test?
A CPU stress test is a diagnostic process used to evaluate the performance, thermal limits, and stability of a central processing unit under extreme conditions.
Purpose of Stress Testing
The main goal of stress testing is to ensure that the CPU can handle intensive tasks, such as gaming, video editing, or large-scale computations, without overheating or crashing. By simulating a high workload, stress tests provide insights into the CPU’s:
- Processing Power: Determines how efficiently the CPU handles computational tasks.
- Thermal Behavior: Analyzes heat generation and the cooling system’s ability to manage it.
- System Stability: Detects any potential issues, such as throttling, instability, or hardware failures.
How It Evaluates Performance and Thermal Limits
During a stress test, the CPU operates at 100% utilization, allowing users to monitor its temperature, clock speed, and power consumption. This data reveals:
- Whether the cooling system is sufficient to maintain safe operating temperatures.
- How well the CPU sustains performance under prolonged workloads.
- Any bottlenecks or inefficiencies in the system.
Also Read: High Cpu Plc Usage – Simple Steps To Boost Performance!
Common Tools for CPU Stress Testing!
A variety of software tools are available to perform CPU stress tests, each catering to different needs and levels of expertise.
Prime95
- Purpose: Known for its rigorous stress-testing capabilities, Prime95 uses complex mathematical calculations to push CPUs to their limits.
- Best For: Identifying stability issues and thermal thresholds.
AIDA64
- Purpose: A comprehensive benchmarking tool that monitors system performance and stability while testing various hardware components.
- Best For: Users seeking detailed diagnostics for both stress testing and system monitoring.
Cinebench
- Purpose: Tests the CPU’s rendering capabilities using real-world scenarios, such as rendering high-resolution 3D scenes.
- Best For: Gamers and content creators looking to evaluate rendering performance.
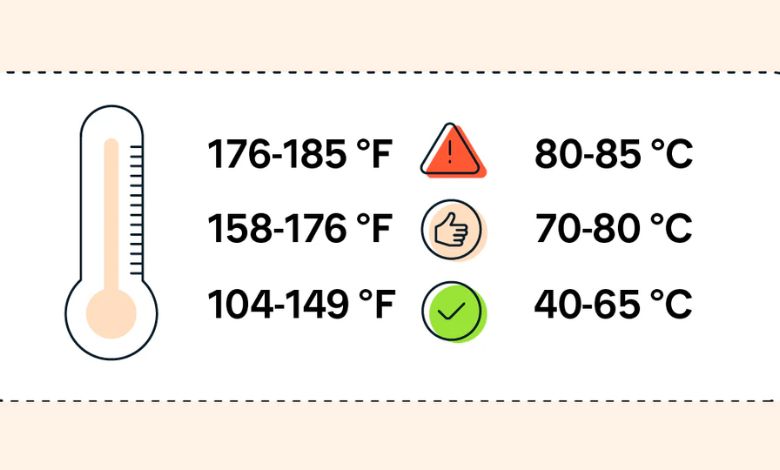
Is 80 Degrees Celsius Safe for Your CPU?
The question of whether 80°C is safe for your CPU depends on factors such as the processor model, cooling system, and workload intensity.
Safe Temperature Ranges for Modern CPUs!
AMD and Intel Guidelines
- AMD Processors: Modern AMD CPUs, such as the Ryzen series, typically operate safely up to 85°C to 95°C, though sustained temperatures close to the upper limit can reduce lifespan.
- Intel Processors: Intel CPUs generally have a safe operating range of 70°C to 80°C, with maximum temperatures often capped at 100°C before thermal throttling occurs.
Variances Based on Processor Models
Each CPU model has its unique thermal specifications, known as the Tjunction Max (maximum operating temperature). For example:
- High-end gaming CPUs may have higher tolerances due to robust design and better cooling.
- Entry-level processors may struggle with prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
Also Read: Does Cpu Affect Psu Needs – Learn How to Choose Right!
Factors Affecting CPU Temperature!
Cooling Systems (Air vs. Liquid)
- Air Cooling: Affordable and reliable, but less effective in handling overclocked or high-performance CPUs.
- Liquid Cooling: Offers superior cooling efficiency, especially for overclocked systems, but requires careful installation and maintenance.
Ambient Room Temperature
The temperature of the room significantly impacts the CPU’s thermal performance. Warmer environments lead to higher operating temperatures, while air-conditioned or well-ventilated spaces help maintain optimal conditions.
Quality of Thermal Paste
Thermal paste facilitates heat transfer between the CPU and the cooler. High-quality thermal paste ensures better thermal conductivity, reducing overall temperatures.
What to Do When Your CPU Reaches 80 Degrees!
If your CPU temperature consistently reaches 80°C or higher during stress tests, it’s essential to take preventive measures to avoid long-term damage or performance degradation.

Monitoring Your System During a Stress Test
Monitoring tools allow you to track the CPU’s temperature and performance in real-time during stress testing.
Software Tools
- HWMonitor: Displays detailed information about the CPU’s temperature, power consumption, and clock speeds.
- CoreTemp: A lightweight tool that focuses on CPU temperature monitoring, providing alerts when temperatures exceed safe limits.
Improving Cooling Efficiency!
Enhancing the cooling system can significantly reduce CPU temperatures and improve overall system performance.
Cleaning Dust from Fans
Dust accumulation in fans and heatsinks reduces airflow, leading to higher temperatures. Regularly cleaning the system ensures optimal cooling performance.
Upgrading Your CPU Cooler
Stock coolers provided by CPU manufacturers are often sufficient for standard use but may struggle under heavy workloads. Upgrading to a high-performance air or liquid cooler can dramatically lower temperatures.
Optimizing Airflow in Your Case
Proper airflow ensures that hot air is expelled from the case efficiently. Tips for better airflow include:
- Using larger or additional case fans.
- Organizing cables to prevent obstruction of airflow.
- Positioning the PC in a well-ventilated area.
Also Read: Steam Deck Gpu Cpu Display – All You Should Know!
FAQS:
Is 80 degrees C too hot for a CPU?
80°C is warm but generally safe for most modern CPUs during heavy use. However, it’s better to keep it below 80°C for long-term health.
What temperature should my CPU be during a stress test?
During a stress test, CPUs can safely run between 70°C and 85°C. If it goes higher, check your cooling setup.
Why does my CPU randomly spike to 80 degrees?
Spikes to 80°C can happen due to sudden heavy tasks or background processes. Poor cooling or old thermal paste might also cause this.
Is 80°C fine for CPU Reddit?
On Reddit, most users agree that 80°C is okay for short periods under load. For long-term use, aim for lower temperatures.
How long can a CPU run at 80 degrees straight?
A CPU can handle 80°C for a few hours, but constant exposure may shorten its lifespan. Keep it cooler for better longevity.
Conclusion
A CPU stress test hitting 80 degrees isn’t necessarily a cause for alarm, as modern processors are built to handle such temperatures under heavy workloads. However, consistently running at this level during extended stress tests may indicate the need for improved cooling or airflow. Maintaining lower temperatures ensures your CPU performs efficiently and lasts longer, making regular monitoring and optimized cooling setups essential for a healthy system.